The SYNERGETICS Innovation Action is aimed at facilitating the green transformation of the existing inland and coastal fleet through the creation of synergies. On the one hand, the objective is to identify and capitalise on synergies with pilot and demonstration projects that are conducted outside of the SYNERGETICS framework. Consortium partners are involved in numerous such projects, which are assessed within Work Package 2, thereby ensuring appropriate cross-linking. On the other hand, the findings from the project’s own demonstrators (Work Package 3) are compared and made available to the industry.
The first deliverable of Work Package 1, D1.1 “Relevant Identified Technical Solutions” documents the outcomes of Task 1.2, which makes an inventory of technical solutions from both within the consortium and external sectors that are promising for reducing energy demand or substituting fossil fuels in waterborne transport. This compilation excludes low Technology Readiness Level (TRL) technologies, such as ammonia and certain battery systems, focusing instead on solutions ready for deployment as per the HORIZON-CL5-2022-D5-01-04 call.
The report begins by reviewing the specific fleets considered and their conditions for adopting greening measures. It introduces the Sustainable Power Portal, developed by the Sustainable Alternative Power for Ships (SAPS) working group of the European Sustainable Shipping Forum (ESSF), which serves as a foundation for SYNERGETICS’ Catalogue of Retrofitting Measures.
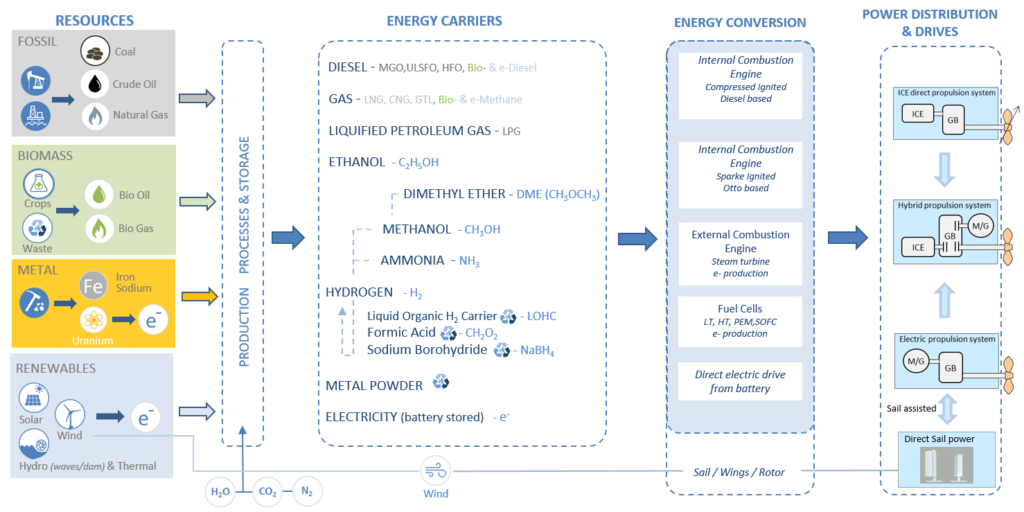
Figure 1 – Sustainable Power Portal
Key technical solutions, including their developments in other sectors, are discussed in Chapter 3. Section 3.2 addresses the topic of energy carriers, while Section 3.3 focuses on the subject of energy converters.
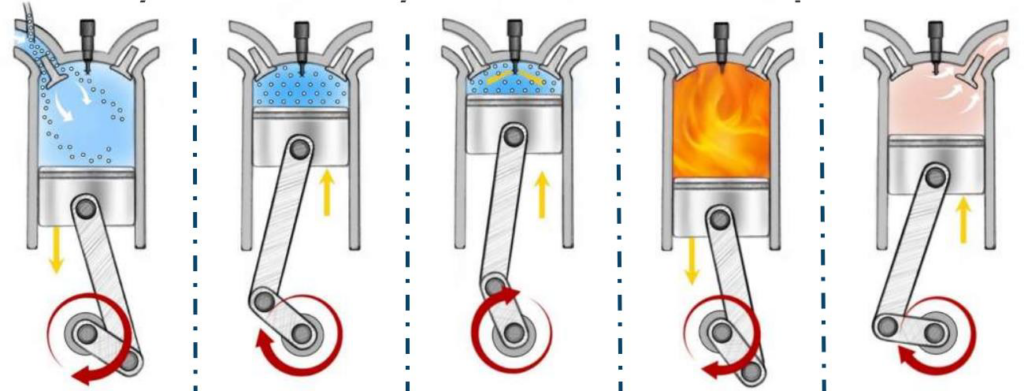
Figure 2 – Hydrogen-Diesel co-combustion in a Diesel-engine
Chapter 4 summarises the relevance of hydrodynamic improvements on energy efficiency and overall emissions.
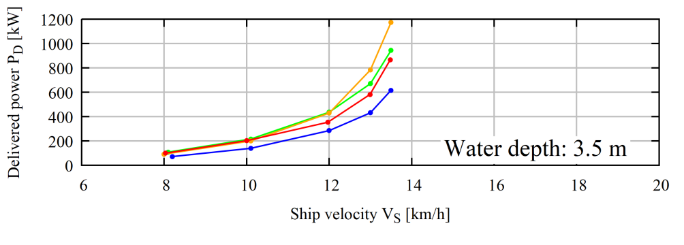
Figure 3 – Delivered power for four different aft ship designs
Shipping remains a hard-to-abate sector, as conditions that drive low-emission technology adoption in other industries, like energy recovery from braking or the use of overhead lines in rail, are hardly to be expected. The pressure to comply with clean air plans is unlikely to be a driving force in shipping. As this is greater in other sectors, it creates a competitive disadvantage for shipping in securing sustainable energy carriers, which are not only limited in availability but also costly and technically challenging to store and convert. Given these barriers, the report advocates marinising high-TRL technologies as a more efficient approach for inland and coastal shipping, along with improving energy efficiency through hydrodynamic optimizations and reducing ship resistance.
In order to surmount the obstacles presented by the high costs, technical and regulatory challenges, and operational drawbacks, the report emphasizes the necessity for holistic strategies that integrate technology development, increased awareness, incentives, and regulations, to facilitate rapid decarbonization.
The required synergy effects are the core topic of the SYNERGETICS project.
The complete report is accessible for download from the Downloads section of the SYNERGETICS’ website.
